Thin Film Polarizers
• Custom-tailored (optimal in terms of extinction ratio, angle of incidence, and damage threshold)
• Types of dielectric coatings: BBAR, V-coatings, dual wavelength coatings, and sharp cut-on and cut-off filters
• Ion Beam Sputtering (IBS) technology treatment is available
• Extinction ratio higher than 10000:1 at a 45° angle of incidence
• Damage threshold higher than 20 J/cm2 at 1064 nm, 10 ns, 100 Hz.
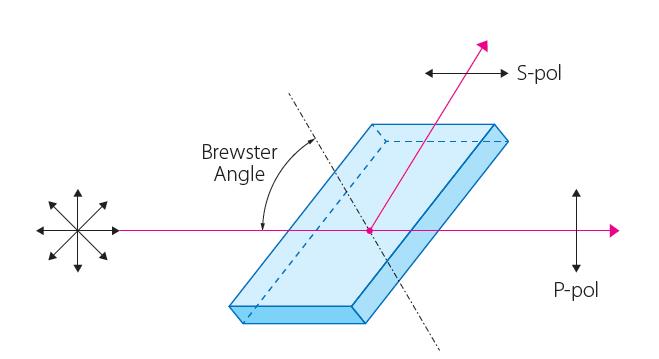
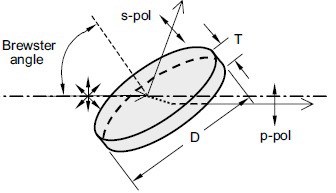
Thin film polarizers are based on interference within a dielectric optical thin-film coating on a thin glass substrate. They are made from composed materials which include a polarizing film, an inner protective film, a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer, and an outer protective film. Thin film polarizers are used for polarization separation, that's to say to change un-polarized beam into linear polarized beam. When the light passes through the polarizer, one of the orthogonal polarization components is strongly absorbed by the polarizer and the other component is weakly absorbed, thus natural light is converted into linearly polarized light.
These polarizers function as beamsplitters, diverting the unwanted polarization 90°. Thin-film plate polarizers have a number of unique advantages, including superior transmission, low scattering and very little wavefront distortion. They can be made with excellent environmental reliability, the highest laser damage threshold and very large aperture sizes. Thin-film plate polarizers function over a specific wavelength range because they are based on multiwave interference and are best suited to laser applications or systems with a limited signal band.
Polarization optics is important for both intra and extra cavity use. By having high contrast thin film polarizers in their design, laser engineers can save weight and volume within their devices without influencing the output. Compared with polarizing prism, polarizer has larger incident angle and can be made with larger apertures. Compared with polarizers made from birefringent crystals, the advantage of thin film polarizers is that they can be made in very large sizes, therefore are particularly well suited for high laser powers and UV wavelengths. Broadband plate polarizers with low dispersions are mainly used in systems that cover a wide wavelength range - for example, in Ti:sapphire fs lasers.
Due to their high damage threshold, thin film polarizers replace Glan laser polarizing prisms or cube polarizing beamsplitter in applications with high energy Nd:YAG applications and in ultrafast lasers.
WISOPTIC Specifications - Thin Film Polarizer
Material | BK7, UVFS |
Diameter Tolerance | +0.0/-0.15 mm |
Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.1 mm |
Clear Aperture | > 90% of central area |
Surface Quality [S/D] | < 20/10 [S/D] |
Transmitted Wavefront Distortion | λ/10 @ 632.8 nm |
Parallelism | ≤ 30” |
Extinction Ratio (Tp/Ts) | > 200:1 |
Coating | High LDT coating upon request |
Laser Damage Threshold | 10 J/cm² @ 1064 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz |