Polarizing Optics for Lasers
WISOPTIC Advantages of Laser Polarizers
• Wide variety of linear polarizers over UV, Visible and IR spectral ranges.
• Linear polarizers include laminated polymer film,
laminated sheet, Polarcor dichroic glass, and Calcite crystal types.
• Antireflective coating (improve transmission, reduce glare, and readability).
• Pigtail (a polarization rotator which has a short length of optical
fiber permanently fixed to a component).
• Broadband connections (has a uniform optical characteristics
over a wide area of the spectrum in the polarization rotator).
Polarizer is a kind of optical filter where the light transmission depends strongly on the polarization state. Normally, light with linear polarization in a certain direction is passed, and light polarized in an orthogonal direction is either absorbed or propagated to a different direction.
For other directions of linear polarization with an angle θ against the“passing”direction, the transmission exhibits a cos2 θ dependence. That can be understood by considering that linear polarization state as a linear superposition of the "passing”and the“blocked”state.
Most polarizers act based on linear polarizations. However, one can also construct devices passing light with a certain circular polarization, usually using one or more quarter waveplates or possibly Faraday rotators in conjunction with a linear polarizer.
Note that a polarizer can not convert any polarization of input light into the wanted polarization; this is physically not possible. It can only remove light with the unwanted polarization.
Polarizer | Material | Illustration | Properties & Application |
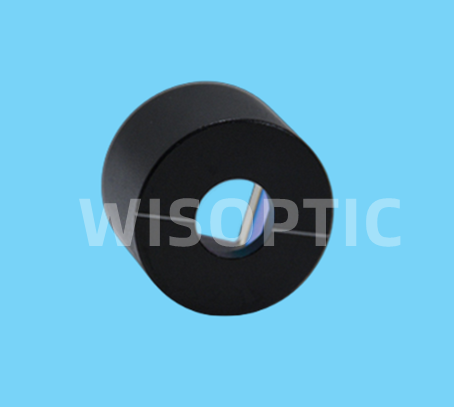
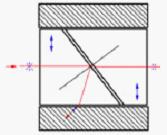
Glan-Taylor Polarizer | α-BBO(190-3500) Calcite(350-2300) YVO4(450-5000) | Air-spaced. Cutting angle close to Brewster ±s Angle. The extraordinary ray passes through straightly with little deviation. Sealed mount without escape windows. Suits for low to medium power application where the rejected beam is not required. | |
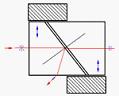
Glan- Laser | α-BBO(190-3500) Calcite(350-2300) | Better than Glan Taylor polarizer. Mounted with escape windows. Suits for high power application. | |
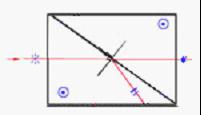
Glan-Thompson | Calcite(350-2300) | Cemented. Suits for low power application. Special design for ratio of L/A (length/aperture) guarantees wide acceptance angle. | |
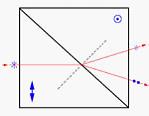
Wollastom | Calcite(350-2300) | Cemented. Both ordinary and extraordinary beams are deviated. Suits for low power application and where large deviation is required. | |
Rochon | α-BBO | Broad wavelength range. |
Comparison of Different Materials of Polarizers
YVO4 | Calcite | α-BBO | Quartz | |
Transparency Band | 500-4000 nm | 350-2300 nm | 220-3000 nm | 200-2300 nm |
Crystal Type (uniaxial) | Positive | Negative | Negative | Positive |
Mohs Hardness | 5 | 3 | 4.5 | 7 |
Thermal Expansion Coefficient | aa=4.43x10-6/K | aa=24.39x10-6/K | aa=4x10-6/K | aa=6.2x10-6/K |